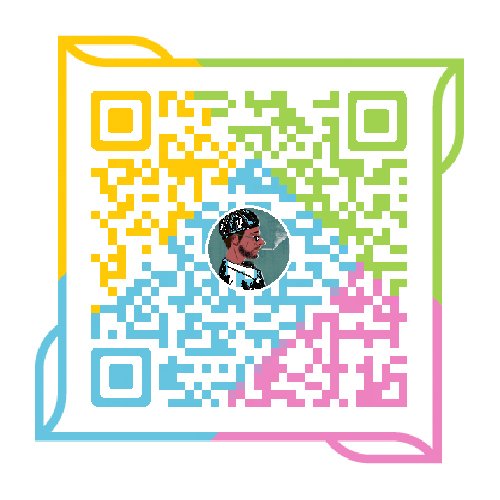
【3.3.1】蛋白质二级结构
蛋白质的二级结构是指多肽链的主链(backbone)部分(不包括R基团)在局部形成的一种有规律的折叠和盘绕,其稳定性主要由主链上的氢键决定。
常见的二级结构有α螺旋(alpha-helix)、三股螺旋(triple helix)、β折叠(beta-sheet)、β转角(beta-turn)、β凸起(beta-bulge)、环和无规则卷曲(random coil)。其中前六种比较有规律。
一、α螺旋
- 最先由Linus Pauling提出,他因此得到第一次诺贝尔奖(Proposed by Linus Pauling, who won his first Nobel Prize).
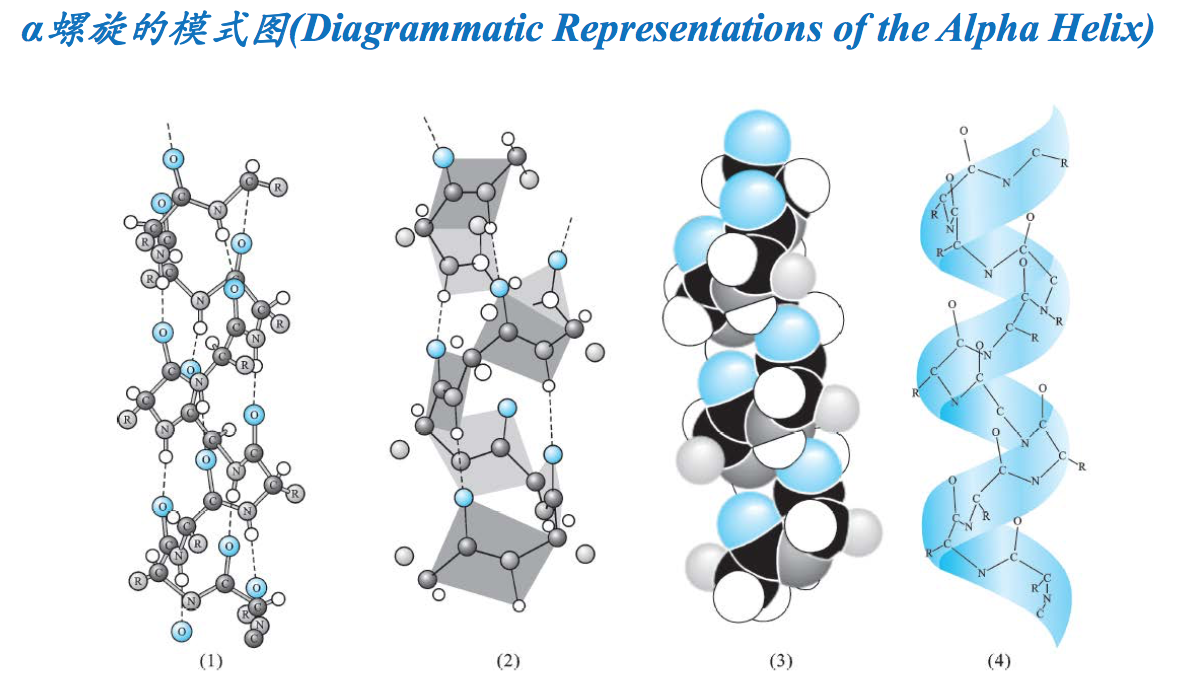
- 为螺旋的结构,肽链主链围绕一个虚拟的轴以螺旋的方式伸展。螺旋的方向几乎都是右手的(The alpha helix is a helical structure. All alpha helices in proteins are almost right-handed)。这是因为蛋白质中的氨基酸只有L型,若形成左手螺旋,L型氨基酸的β碳和羰基氧在空间上会发生冲突,其稳定性会降低。
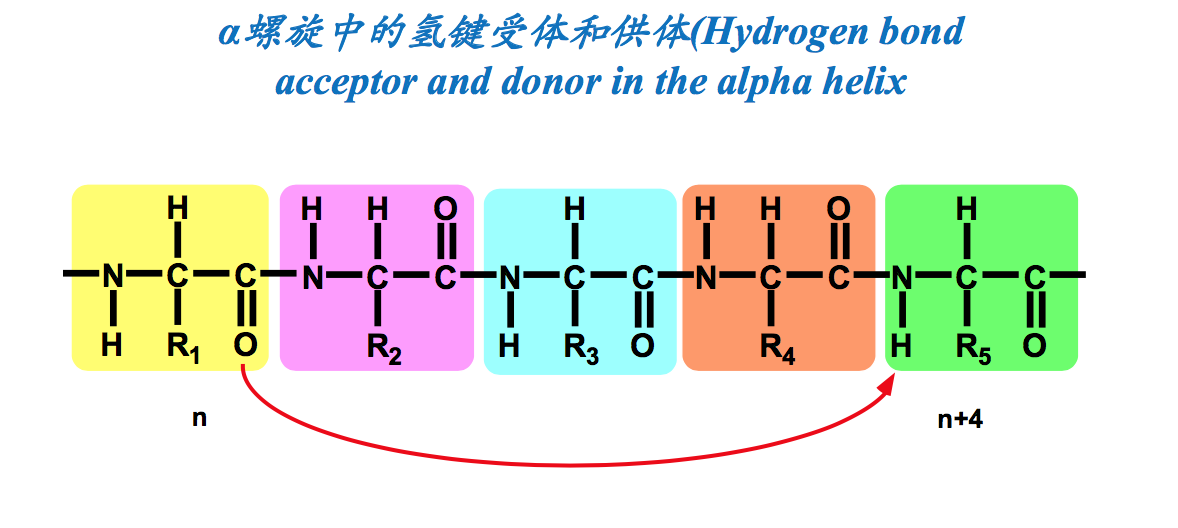
- 由主链上的氢键稳定,氢键构成的样式为n位残基的羰基O与n+4位的酰胺N上的H形成氢 键(Stabilized by backbone hydrogen bonds. H-bond patterns of the alpha helix: Carbonyl oxygen of the nth residue forms H-bond with amide hydrogen of the (n+4)th residue).螺旋的形成是自发的,主要由主链上的氢键来稳定。氢键在n位氨基酸残基上的C=O与n+4位残基上的N-H之间形成。被氢键封闭的环共含有13个原子,因此α螺旋也称为3.613螺旋。螺旋的前、后4个氨基酸残基通常不能形成全套螺旋内氢键,这些残基需要与水分子或蛋白质内部的其他基团形成氢键后才能稳定下来。
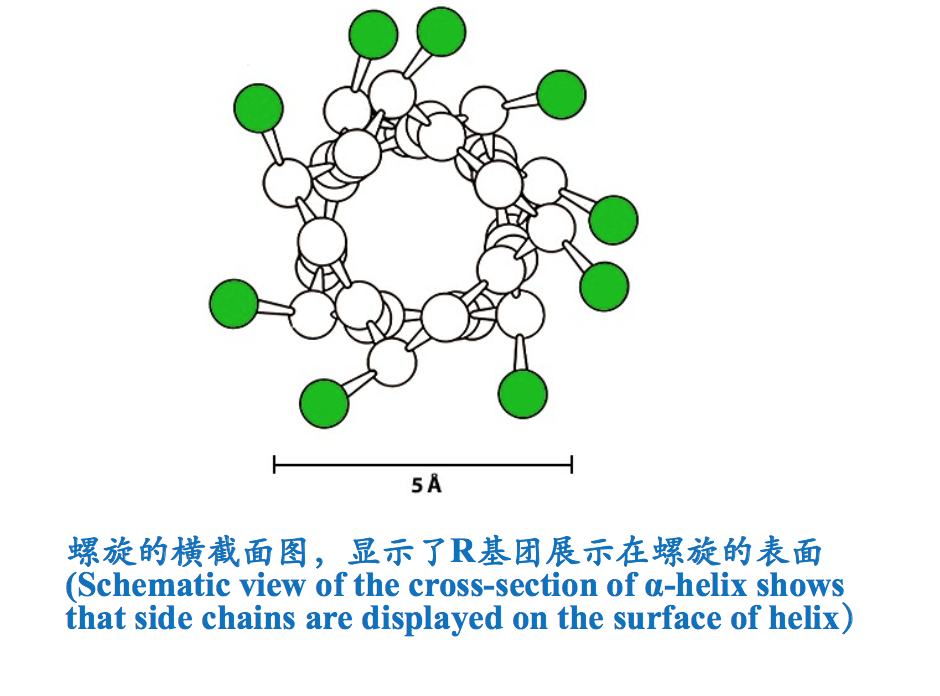
- R基团展示在螺旋的表面(R groups are displayed on the surface of the helix).氨基酸残基的R基团伸展在螺旋的表面,虽不参与螺旋的形成,但其大小、形状和带电状态却能影响到螺旋的形成和稳定性
- 不同的氨基酸形成螺旋的倾向性有别,Glu、Met、Ala和Leu等有利于形成α螺旋,而Pro 和Gly则不利(Helix propensity of an AA is a measure of the likelihood for the amino acid to be in a helix; Glu, Met, Ala, Leu have high propensities; Proline and Gly usually don’t favor formation of α-helix).
- 螺旋有关的参数有:每圈3.6个氨基酸,螺距为0.54nm,每个氨基酸上升的距离是0.15nm, Φ和Ψ分别是-60 和-45 度(Some parameters about the alpha helix: Residues per turn: 3.6 Rise per residue: 0.15 nm Rise per turn (pitch): 3.6 ×0.15nm = 0.54 nm,p hi = -60 degrees, psi = -45 degrees)。螺旋的半径为0.23nm,二面角(ф,ψ)约为(-57 º,-47 º)。
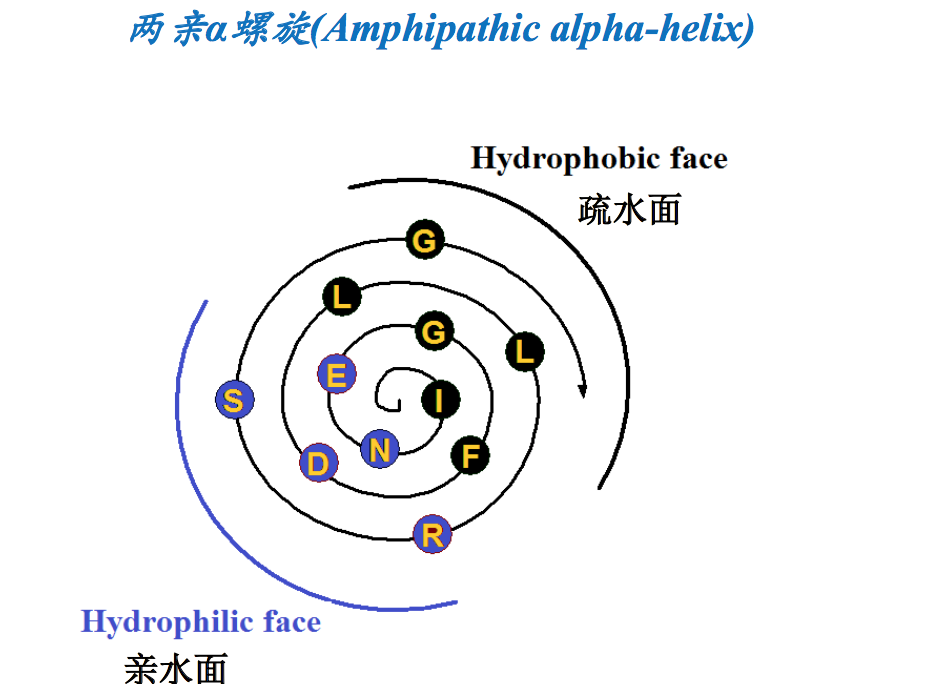
- 可能是亲水的,疏水的或者是两亲的(Can be hydrophilic, hydrophobic or amphipathetic).
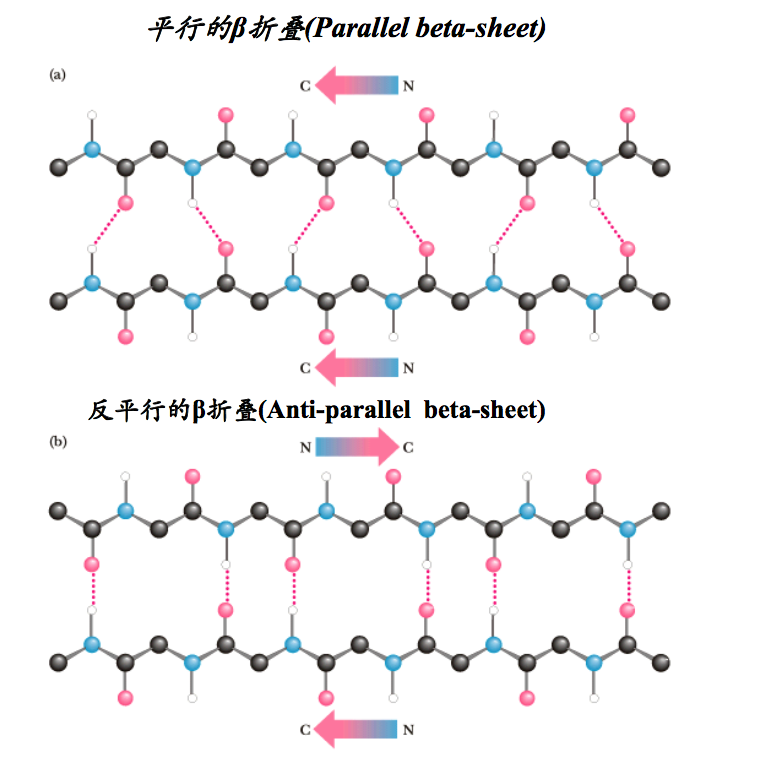
二、β折叠(The Beta-Pleated Sheet or Beta Sheet)
β折叠又称为β折叠片层,这是Pauling和Corey继发现α螺旋结构后,同年发现的又一种重要的蛋白质二级结构。
与α螺旋相比,β折叠是肽链的一种更加伸展的结构,主链呈扇面状展开。其主要特征包括:
(1)肽段几乎完全伸展,肽平面之间成锯齿状。
(2)相邻肽段呈现平行排列,相邻肽段之间的肽键形成氢键,其中的每一股肽段称为β股(β strand)。至少由2个β股组成
(3)R基团垂直于相邻两个肽平面的交线,并交替分布在折叠片层的两侧。
(4)肽段的走向有正平行和反平行两种。正平行经常简称为平行,指相邻β股的N-端位于同侧,反平行正好相反。在反平行折叠中,氢键的三个原子(N-H-O)几乎位于同一直线上,因此反平行折叠更加稳定,其存在的机会就更大。
(5)反平行β折叠的每一个氨基酸残基上升0.347nm,二面角(ф,ψ)约为(-135º,+140º),平行β折叠的每一个氨基酸残基上升0.325nm,二面角(ф,ψ)约为(-120º,+105º)。
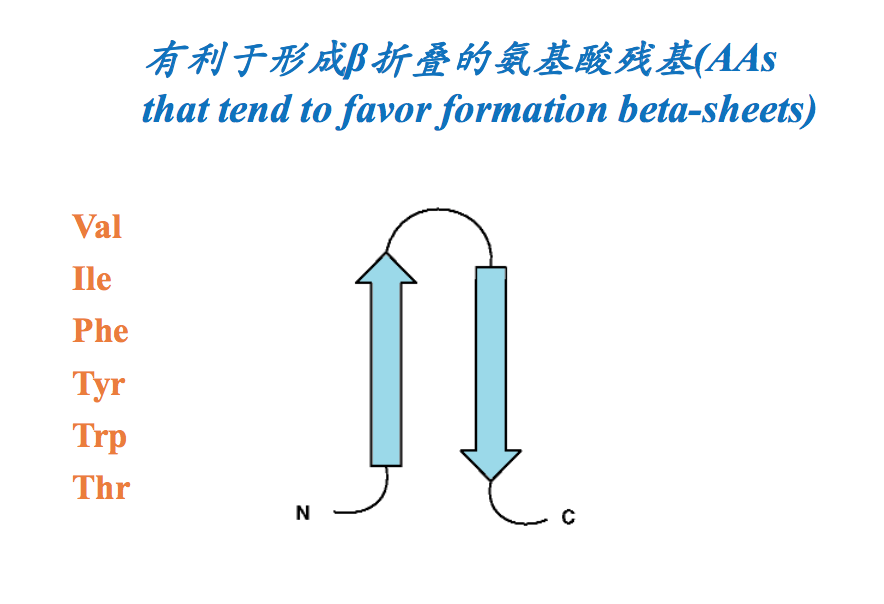
- 有的氨基酸残基有利于形成β折叠(Some AAs tend to form the beta-sheet).

三、β转角(The Beta Turn)
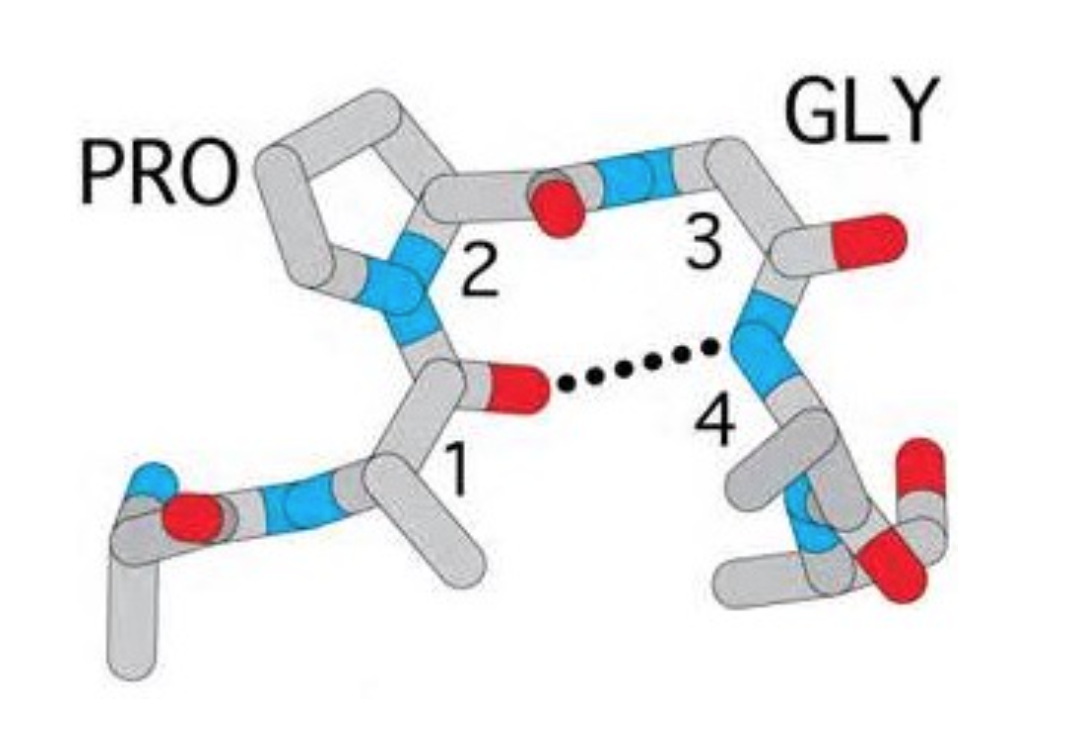
β转角也称β弯曲(beta-bend)、β回折(beta-reverse turn)、紧密转角(tight turn)或发夹结构(hairpin structure)。这种结构是指伸展的肽链形成180 º的U形回折。其主要特征包括:
- 由4个氨基酸残基组成(第1个编号为n,第4个则为 n+3),其中n位的羰基O和n+3位的酰胺N上的H形成氢 键(Is composed of four successive amino acid residues. The carbonyl oxygen of the nth residue forms H-bond with the amide proton of the (n+3)th residue).
- 形状像英文字母U,因此可导致肽链主链发生180°方 向的改变(It looks like English letter U and can cause 180 degree change of direction of the backbone).
- 富含脯氨酸和甘氨酸的四个氨基酸更容易形成β转角 (Proline and glycine have high propensity for beta turns)
- 有利于形成反平行的β折叠(Promotes formation of antiparallel beta sheets).
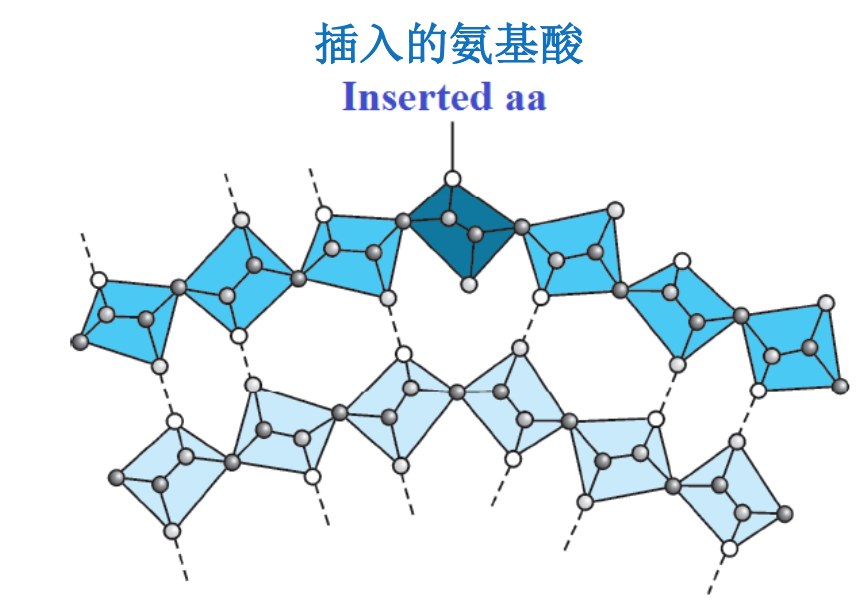
四、β突起(The Beta Bulge)
β突起可视为在一个正常的β折叠的β股之中引入一个额外的氨基酸残基以后对 原来结构造成的一种局部的破坏。它更容易发现在反平行的β折叠之中(A beta bulge can be regarded as a localized disruption of the regular hydrogen bonding of beta sheet by inserting extra residues into one or both H-bonded β-strands and is more frequently found in the antiparallel β-sheet).
β突起可以轻微地改变肽链的走向,从而影响到蛋白质的结构和功能(β-bulge can change direction of the β-strand slightly and then affect structure and function of proteins)
参考资料
- 南京大学 杨荣武老师 《结构生物学》课件
